
Detroit’s aerospace manufacturing scene has come a long way—from helping out with Apollo missions to crafting critical parts for today’s space exploration efforts.
The city draws on decades of precision manufacturing and strong partnerships with big-name aerospace contractors, supplying NASA’s Artemis program and plenty of commercial space ventures.
Back in the 1950s, Detroit’s automotive know-how played a key role in America’s push into space.
Michigan companies really stepped up for the Apollo program from 1958 to 1969, using their manufacturing chops to help build those massive Saturn V rockets that sent astronauts to the moon.
When the city shifted from cars to aerospace, it just made sense.
Detroit’s precision metalworking skills fit perfectly for rocket components and spacecraft parts.
Local manufacturers started developing custom tools for tough aerospace jobs.
Today, more than 78 Michigan companies support NASA’s Space Launch System program.
Together, they’ve landed over 80 contracts with NASA, totaling more than $37 million.
Michigan’s also produced 12 NASA astronauts—pretty impressive—and keeps up strong connections to space exploration projects.
Detroit’s aerospace manufacturing base covers a lot of ground.
You’ll find both big contractors and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) here, from precision tooling experts to advanced materials suppliers.
Detroit brings some unique perks to the table for space manufacturing.
The region’s workforce knows complex manufacturing inside and out, thanks to decades in the auto industry.
Workers can easily adapt their metalworking and assembly skills for aerospace needs.
Detroit’s got the infrastructure, too.
Large-scale production facilities and specialized tooling are everywhere, and the city’s transportation network makes it easy to move oversized parts to launch sites.
A lot of Detroit manufacturers serve both commercial aerospace and defense sectors.
This dual focus helps keep revenue steady and encourages technical cross-pollination.
Major aerospace contractors are drawn here by the local engineering talent.
Companies like Boeing team up with Detroit firms for specialized tooling and components, blending global aerospace know-how with Detroit’s manufacturing edge.
Futuramic Tool & Engineering stands out as a modern Detroit success story in space manufacturing.
They run factories in Detroit and Warren, making critical tools for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
Futuramic delivered specialized equipment that sped up SLS core stage production at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility.
The company built tools for the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank—the biggest piece of the SLS core stage.
That tank holds over 700,000 gallons of propellant and needs super-precise handling gear.
Futuramic’s horizontal joining tool lets teams assemble it faster than old-school vertical stacking ever could.
Boeing tapped Futuramic to design and make tooling for several SLS components, including tank domes, intertank sections, and test simulators.
These tools help create the most powerful rocket since Saturn V.
Michigan’s also planning a new vertical-launch spaceport, aiming to create up to 40,000 jobs by 2025.
This site would handle both government and commercial space launches, showing Detroit’s determination to move beyond just making parts and get into launch operations too.

Detroit is home to several major aerospace contractors who contribute to both commercial space programs and defense efforts.
You’ll find everything from established defense giants with local operations to niche equipment manufacturers supporting spacecraft development.
Lockheed Martin has a strong presence in metro Detroit, focusing on advanced manufacturing and systems integration.
Their Michigan teams contribute to space exploration projects, including parts for NASA’s Orion spacecraft and various satellite systems.
Northrop Grumman works through partnerships and supply chain relationships in the area.
They lean on Detroit’s manufacturing expertise for aerospace components and defense systems, including advanced materials and propulsion tech for both military and commercial space.
Both companies take advantage of Michigan’s skilled workforce and robust manufacturing infrastructure.
They work with local suppliers and schools to develop the next generation of aerospace technology.
Their presence bolsters Detroit’s role in the national defense supply chain.
The Boeing Co stays active in Michigan through manufacturing partnerships and supplier deals.
Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft program counts on Michigan suppliers for key components and systems.
The company collaborates with local manufacturers to produce parts for both commercial aircraft and space systems.
Moeller Aerospace plays a big role as a supplier in Detroit’s aerospace ecosystem.
They focus on precision manufacturing and component production for major aerospace contractors, offering advanced machining and assembly services for both commercial and defense markets.
These partnerships build a sturdy supply chain supporting multiple space programs.
Local manufacturers get access to Boeing’s technical standards, which helps Detroit stay competitive in aerospace manufacturing.
Testek Solutions shows off Detroit’s growing aerospace test equipment sector.
They develop specialized testing systems for spacecraft components and propulsion systems, making sure equipment is reliable and safe for commercial space missions.
Aerospace test equipment makers in Detroit serve several markets:
Other local innovators include Airspace Link, which builds digital infrastructure for drone operations.
Their cloud-based platform helps integrate drones safely into airspace, adding to Detroit’s aerospace tech scene.
Detroit Defense provides technical services and logistics support for military systems, highlighting the city’s diverse aerospace capabilities.
These companies show how Detroit is shifting from traditional manufacturing toward advanced aerospace technologies.
They support both established space programs and new commercial ventures.
Detroit’s space and defense manufacturing sector blends decades of precision engineering with today’s aerospace technology.
Manufacturers here turn out critical parts for spacecraft, satellites, and defense systems using advanced production methods and specialized assembly processes.
Detroit manufacturers focus on high-precision parts for spacecraft and satellite systems.
Their facilities turn out critical pieces like guidance system housings, thruster assemblies, and structural components that have to survive the harshness of space.
Local companies use advanced materials such as titanium alloys and carbon fiber composites.
These materials offer the strength-to-weight ratio spacecraft need.
They use computer-controlled machining and automated quality testing to get the job done.
Defense manufacturing in Detroit produces components for military satellites and space-based defense systems.
Companies work directly with the Department of Defense to create specialized hardware for national security.
They hold themselves to quality standards that go beyond typical aerospace requirements.
Every part gets put through its paces—thermal cycling, vibration analysis, vacuum chamber validation—to make sure it’s ready for space.
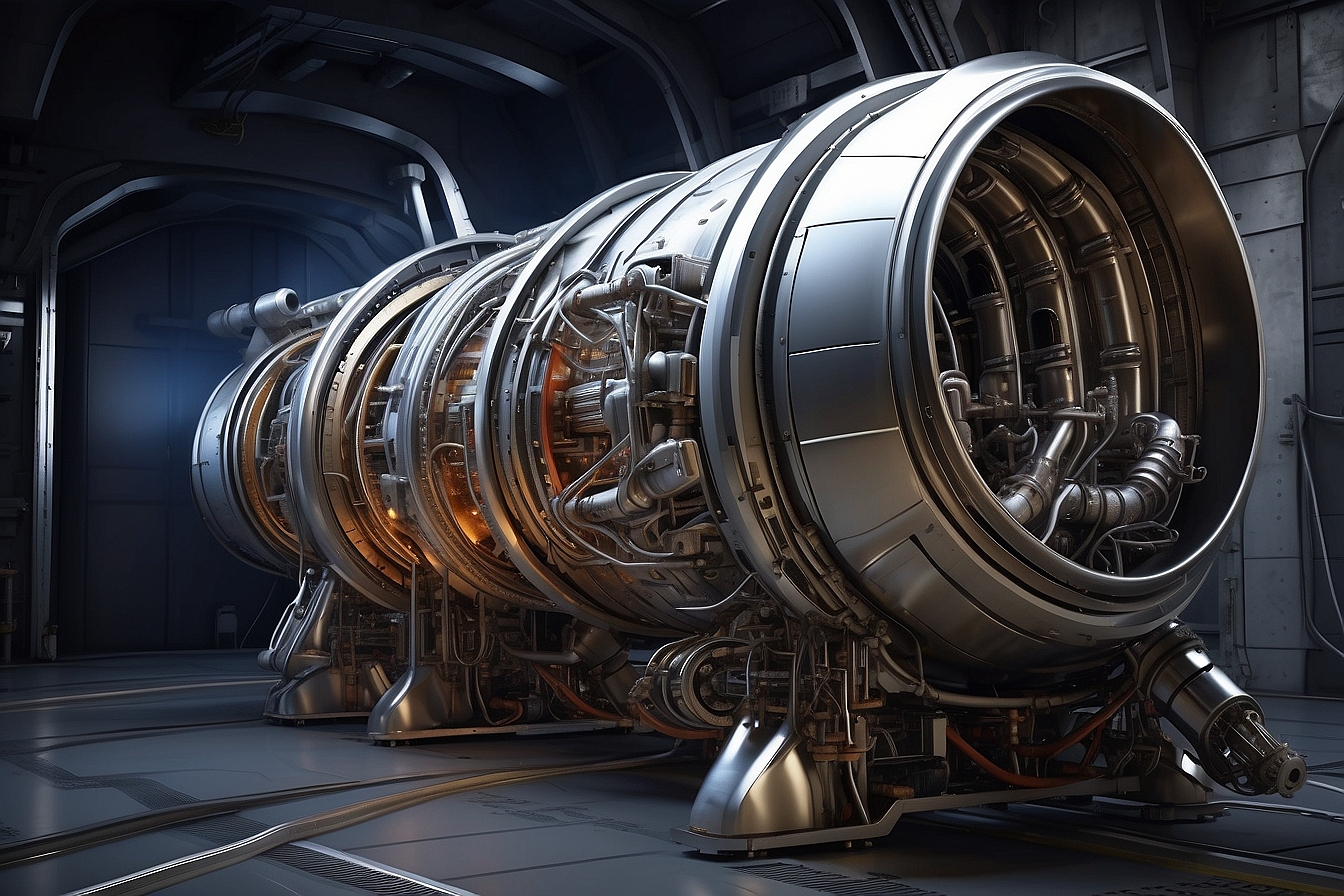
Detroit’s turbine engine expertise stretches from cars to space propulsion.
Manufacturers here produce precision-machined parts for rocket engines and spacecraft propulsion units.
Companies make turbine blades, combustion chambers, and fuel injection systems for space.
These parts need extreme precision—tolerances down to thousandths of an inch.
Advanced CNC machining centers handle the tricky geometries.
Heat-resistant alloys are the backbone of these components.
Manufacturers use materials that can handle temperatures above 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit and still hold up in the vacuum of space.
Testing involves high-temperature cycling and pressure checks.
Every component goes through thousands of simulated cycles before it ever gets approved for flight.
Detroit’s precision machining shops use multi-axis CNC equipment and coordinate measuring machines to nail the tight tolerances space hardware demands.
They handle everything from prototypes to production runs for spacecraft components.
Assembly teams put together multiple precision parts into subsystems.
Technicians work in cleanrooms to keep sensitive space hardware free from contamination.
Click-Loc® technology and similar quick-connect systems make sure connections are reliable in space.
Specialized tools let technicians assemble parts that have to work in zero gravity.
Assembly processes account for the thermal expansion and contraction cycles that happen during space missions.
Quality control tracks every part through the process.
Digital documentation ensures you can trace everything from raw materials to final assembly, meeting both NASA and Department of Defense standards.
Detroit uses its century-old manufacturing know-how to produce critical military aircraft systems and build strategic partnerships with the U.S. Department of Defense.
The city delivers innovative sustainment solutions that cut military equipment downtime from years to just weeks.
Detroit’s aerospace manufacturers make essential parts for military aircraft across all service branches.
Factories here turn out precision parts for fighter jets, transport planes, and unmanned aerial vehicles for the U.S. Air Force and Navy.
Local companies focus on advanced metallic production at places like the LIFT Advanced Metallic Production and Processing Center.
This Department of Defense-backed institute develops cutting-edge materials for military aerospace uses.
Detroit manufacturers build electronic warfare systems and avionics packages too.
These systems protect military planes from enemy radar and missiles during combat.
The city’s auto expertise translates well to military vehicles.
Ground Vehicle Systems Center teams develop and test armored vehicles, tanks, and specialized military transports for the U.S. Army.
LIFT partners closely with the U.S. Department of Defense Office of Naval Research.
They focus on new manufacturing processes for military uses and work to strengthen America’s defense industrial base.
Detroit-area companies join the Army Transformation Initiative, connecting traditional defense contractors with tech startups to speed up military capability development.
The Ground Vehicle Systems Center acts as a main DoD research site.
Military officials often visit Detroit to check out new tech, like virtual reality training systems and AI-powered defense applications.
Newlab Detroit links defense tech startups with established military contractors.
This innovation hub gets support from private companies and government partners focused on national security.
Detroit facilities offer rapid repair solutions for deployed military equipment.
The Ground Vehicle Systems Center recently reverse-engineered critical Patriot missile system parts using 3D printing.
Traditional suppliers quoted 900 days to replace damaged Patriot system tubing.
Detroit engineers got it done in 45 days by using advanced manufacturing techniques.
That speed is crucial for military readiness.
Repairs that used to take years now wrap up in weeks, keeping weapon systems up and running during deployments.
Detroit’s sustainment capabilities go beyond one-off repairs.
Manufacturers here keep production lines running for spare parts, ammunition, and specialized military gear for all service branches.
Detroit’s space manufacturing sector leans heavily on 3D printing and advanced composite materials to make spacecraft parts efficiently.
These technologies help cut material waste and allow for complex geometries that traditional manufacturing just can’t pull off.
Space manufacturers in Detroit now use additive manufacturing to build critical spacecraft components faster and at lower cost. Engineers can make complex internal structures and lightweight designs that traditional machining just can’t pull off.
This tech really shines when it comes to low-volume, high-complexity parts—the kind you see all the time in space. Metal 3D printers crank out rocket engine bits, while plastic additive manufacturing turns out satellite housings and various interior parts for spacecraft.
Detroit facilities get a boost from suppliers who bring in specialized space-grade materials. These materials actually meet the tough aerospace standards for strength, temperature resistance, and outgassing needed for space.
Events like RAPID + TCT in Detroit highlight the latest additive manufacturing tech for aerospace. Local manufacturers meet equipment and materials suppliers there, and it’s a pretty good way to stay on top of what’s new.
Rapid prototyping comes standard with this technology. Engineers test out several design versions quickly, all before investing in expensive tooling for traditional processes.
Composite materials pack lightweight properties and impressive strength, making them perfect for spacecraft structures. Detroit manufacturers use carbon fiber, fiberglass, and ceramic matrix composites for everything from satellite panels to rocket fairings.
They’ve adopted advanced techniques like automated fiber placement and resin transfer molding. These methods keep quality consistent and cut down labor costs compared to old-school hand-layup.
Manufacturers are combining 3D printing with composite manufacturing to make hybrid parts. They print complex internal structures, then wrap them in composite materials for extra strength and thermal protection.
Quality control systems track each composite part from raw materials to final assembly. This traceability lines up with NASA requirements and helps ensure reliable performance in space.
Detroit’s automotive background means the city already has skilled workers who know composite materials. That expertise slides right into space manufacturing, usually without much extra training.
Space manufacturers in Detroit blend additive and composite technologies into single workflows these days. By doing this, they cut assembly time and remove failure points that used to show up between separate components.
Digital manufacturing systems now control both 3D printing and composite laying at once. Computer models drive production directly, so specs stay exact and manual errors drop.
Automated inspection systems—things like laser scanning and ultrasonic testing—check component quality during production. These systems catch defects early, which saves money on waste and rework.
Production facilities use modular equipment setups that switch quickly between different parts. That flexibility helps manufacturers move from satellite components to spacecraft parts without much hassle.
With these technologies, companies can do just-in-time manufacturing for space missions. They make components closer to launch dates, so storage costs drop and last-minute design tweaks are possible.

Space manufacturing companies in Detroit have to meet strict industry certifications and federal requirements. These standards keep safety and reliability front and center in commercial space operations.
Space manufacturers in Detroit aim for AS9100 certification as the main quality standard. This aerospace-specific standard builds on ISO 9001 and adds crucial safety and traceability steps.
AS9100 covers:
Detroit facilities also get ITAR registration for defense-related space parts. Companies like Ford’s aerospace division and newer space startups keep these certifications to work with NASA and commercial partners.
Getting certified usually takes 12-18 months for a new facility. External auditors check out design processes, manufacturing controls, and documentation before giving the green light.
Quality assurance teams in Detroit’s space facilities run tough testing protocols at every stage. They check materials, measure dimensions, and validate performance before anything leaves the building.
Key QA steps:
Manufacturers use digital tracking systems to keep full traceability records. Each part gets a unique ID that links back to its materials, tests, and production crew.
If a part doesn’t meet standards, it goes straight into quarantine. Quality engineers dig into the root cause and fix the problem so it doesn’t happen again.
Federal Aviation Administration regulations cover commercial space activities in Detroit. Companies have to get launch licenses and prove vehicle safety before they can operate.
Main federal requirements:
Detroit space manufacturers also follow NIST cybersecurity frameworks to protect sensitive data. This matters more as companies handle classified defense contracts.
Regular audits check for ongoing compliance. If a company doesn’t comply, it could lose its license or contracts, so staying up to code is non-negotiable.
Detroit’s space manufacturing sector is all in on advanced digital technologies for precise spacecraft components and systems. Modern facilities run digital twins for real-time monitoring, use automated robotics for tricky assemblies, and set up tight cybersecurity to guard aerospace data.
Digital twins give engineers virtual copies of real spacecraft manufacturing processes. These computer models match up with Detroit’s actual production lines.
Engineers test out changes on digital twins before making them real. The virtual models show the effects on speed and quality, which helps avoid costly mistakes on the floor.
Real-time monitoring links physical sensors to digital models. Data like temperature, pressure, and vibration flows straight from the factory into computer simulations. Operators can catch issues before they slow down production.
Space component makers use digital twins to fine-tune complex processes. Rocket engine parts need super-tight tolerances, and digital models help keep everything on track.
Simulation software lets engineers try out new manufacturing techniques virtually first. They can experiment with assembly order, tool paths, and quality checks. This speeds up improvements while keeping things safe.
Suppliers in Detroit use digital twins to predict equipment maintenance needs. The virtual models track machine wear and performance, so maintenance happens before breakdowns mess up production.
Automated systems now handle repetitive work in Detroit’s space manufacturing plants. Robotic arms weld, machine, and assemble with reliable precision.
Industrial robots team up with human technicians on spacecraft assembly. Robots handle tasks that need exact positioning and force, while people focus on problem-solving and quality checks.
Automated material handling systems move parts through the factory. Conveyors and autonomous vehicles shuttle components between stations, cutting down on manual lifting and keeping things moving quickly.
Quality control automation uses cameras and sensors to inspect finished parts. Computer vision spots surface defects, dimensional errors, and material flaws. Automated checks go faster than manual ones and still catch the details.
Programmable logic controllers run multiple manufacturing processes at once. These systems handle timing, sequencing, and safety across production lines. This stops conflicts between operations before they start.
Machine learning algorithms help robots get better over time. The systems look at production data to boost speed, accuracy, and energy use. Smart automation changes with production needs, and you don’t have to reprogram everything from scratch.
Manufacturing cybersecurity protects spacecraft designs and production data. Detroit facilities set up several security layers to block unauthorized access.
Network segmentation keeps manufacturing systems separate from corporate networks. Critical equipment runs on its own secure networks, limiting the fallout if there’s an attack.
Access controls set permissions by job role. Technicians can run certain machines, but only engineers get to the design files, and even then, they need extra authentication.
Data encryption secures info moving between systems. Design files, schedules, and quality data get encrypted in transit and at rest. This helps stop data from getting intercepted.
Continuous monitoring looks for odd network activity. Security software tracks logins, data transfers, and changes to systems. Alerts go out to security teams if something seems off.
IT teams regularly update manufacturing software to fix known security holes. They test updates on isolated systems first to avoid breaking anything in production.
Employee training covers cybersecurity basics for the shop floor. Workers learn to spot phishing, use strong passwords, and report anything weird. Honestly, human awareness is the first line of defense.

Detroit’s space manufacturing scene thrives thanks to solid design-for-manufacturing practices and specialized innovation hubs. These places give aerospace companies the tools and space they need to develop everything from satellite parts to full spacecraft systems.
Space companies in Detroit use design for manufacturing (DFM) to cut costs and boost quality. The focus is on making parts that fit Detroit’s existing industrial strengths.
Local aerospace manufacturers use DFM to optimize designs before production even starts. This reduces material waste by up to 30% and shaves a lot of time off manufacturing.
Companies design space parts with Detroit’s precision machining and automated assembly know-how in mind. They play to the region’s strengths.
Key DFM benefits:
Companies can test manufacturing processes early in the design phase. This helps avoid expensive changes later and makes sure parts meet aerospace standards.
Detroit’s space manufacturing boom depends on partnerships with private companies, universities, and government groups. These collaborations bring funding, expertise, and testing facilities to the table.
The University of Michigan teams up with aerospace companies to develop new materials and techniques. Students get hands-on experience with real industry projects while earning their degrees.
Michigan Central is home to nearly 240 companies working on advanced technologies. Since 2023, startups there have pulled in close to $700 million in funding.
Partnerships offer:
Federal agencies also work with local manufacturers to test new space tech. These programs help companies meet NASA and military specs.
Knowledge bars and APEX accelerators give targeted help to space manufacturing startups and established companies. They offer technical support, business development, and chances to network.
The knowledge bar connects manufacturers with advisors who know aerospace inside out. Companies can get advice on materials, processes, and certifications.
APEX accelerators zero in on manufacturing excellence. They help companies boost efficiency and hit strict aerospace quality marks.
These programs offer hands-on help for companies new to space manufacturing. Participants get guidance on supply chain management and regulatory compliance.
Detroit’s accelerator programs have guided dozens of companies from prototype to production. Many have landed contracts with major aerospace primes.
Companies also benefit from peer learning here. They swap best practices and tackle common manufacturing challenges together.

Detroit’s space manufacturing sector taps into a deep pool of engineering talent and strong university partnerships to build specialized training programs. Companies work with local schools to develop courses that fit the real needs of spacecraft and satellite production.
Detroit draws engineers from the auto industry, and they bring valuable manufacturing know-how to space projects. The workforce has skills in precision manufacturing, materials science, and systems integration.
Many professionals make the jump from automotive to aerospace since both fields need similar technical chops. Advanced manufacturing processes from car production work just as well for spacecraft parts.
The region benefits from decades of investment in technical education. Community colleges offer programs in machining, welding, and quality control—exactly what space manufacturers need.
Local companies say there’s strong demand for mechanical engineers, manufacturing techs, and quality assurance specialists. With the auto industry’s downsizing, a lot of experienced workers are ready for new opportunities in space manufacturing.
Universities in Southeast Michigan build targeted programs to support space manufacturing. Wayne State, University of Michigan, and Lawrence Tech lead the way.
They offer specialized courses in spacecraft design, satellite systems, and space-grade materials. Students use the same equipment found in real production facilities.
Industry partners help keep coursework current with new tech. Companies provide feedback on skills needed and offer internships that connect students to jobs.
Research collaborations between universities and manufacturers push new technologies forward. Faculty work on projects ranging from lightweight composites to automated assembly systems.
The Michigan Space Grant Consortium leads efforts across the state to expand aerospace education. They connect K-12 schools with space industry professionals, hoping to spark interest in the next generation.
Manufacturing bootcamps and certification programs give current workers a way into space sector jobs. These programs focus on practical skills like clean room procedures and meeting space-grade quality standards.
Professional development keeps the workforce up to speed as technology changes fast. Companies put money into continuing education so their teams stay sharp on new materials, processes, and regulations.
Apprenticeship programs blend classroom learning with real-world experience. Workers pick up the specialized skills space manufacturing needs while earning solid wages.

Detroit throws some of the biggest aerospace manufacturing events around. These gatherings connect space industry suppliers with defense contractors and government agencies.
The AeroDef Manufacturing conference at Huntington Place brings in top aerospace companies. Partnerships with advanced manufacturing forums create even more networking opportunities for space-focused businesses.
AeroDef Manufacturing 2025 lands at Detroit’s Huntington Place from April 8-10, 2025. The event dives deep into aerospace and defense industries—covering land, air, sea, and space.
Over three days, attendees check out advanced tech exhibits and catch educational sessions with industry experts. Major aerospace companies like BAE Systems, Bell Textron, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, RTX, and Boeing steer the event content.
Government reps from the U.S. Army, Navy, Air Force, and Space Force join private contractors at the event. They tackle big issues such as supply chain resiliency, manufacturing optimization, and funding.
New sessions this year spotlight automation assembly, robotics, and sustainment solutions for military gear. The Michigan Alliance of APEX Accelerators sponsors a Knowledge Bar to help suppliers go after federal government contracts, including those tied to space.
AeroDef Manufacturing teams up with three other major industry events for even bigger networking. RAPID + TCT stands out as North America’s top additive manufacturing and industrial 3D printing conference.
The World Congress Experience (WCX) focuses on innovation in mobility technologies. America Makes’ Spring Technical Review and Exchange (TRX) emphasizes additive manufacturing and education partnerships.
Together, these events create a massive exhibit floor packed with the latest in manufacturing tech. Attendees get access to audiences interested in aerospace, defense, and advanced manufacturing.
The combined events show how different manufacturing fields influence one another. Space manufacturing companies get a front-row seat to new 3D printing and mobility tech that could reshape spacecraft development.
These collocated events draw in key players from aerospace, defense, and advanced manufacturing. Companies meet potential suppliers, customers, and tech partners from all over.
Detroit’s manufacturing comeback brings extra networking chances outside formal conferences. The city now attracts Silicon Valley tech firms, military contractors, aerospace companies, and even nuclear energy folks.
Business development opportunities range from federal funding talks to supply chain partnerships and manufacturing capability assessments. The Knowledge Bar helps companies navigate the federal contracting maze.
Space manufacturing companies find Michigan-based suppliers and can link up with established automotive manufacturers moving into aerospace. These events bridge traditional aerospace giants and up-and-coming space industry players.

Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) really drive Detroit’s growing space manufacturing scene. They deliver specialized parts and clever solutions that big aerospace contractors need for space missions.
Detroit’s SMEs shine at making precision parts for spacecraft and satellites. They turn out crucial pieces like guidance system housings, thruster components, and thermal protection materials.
Many small manufacturers use Detroit’s automotive know-how to build space-grade products. They rely on advanced metal forming to make lightweight structures. Their precision machining hits the tight tolerances aerospace demands.
Local SMEs often carve out niche markets that bigger companies skip. They create custom solutions for unique spacecraft needs. These companies can shift production quickly to meet new requirements.
Key specialized areas include:
Small and medium manufacturers fuel economic activity in Detroit’s space sector. They generate high-paying jobs for skilled workers and engineers, often paying above the regional average.
SMEs strengthen the local supply chain by buying materials from nearby sources. Their purchases boost other businesses, creating a multiplier effect in the regional economy.
These companies also attract talent to Detroit. Engineers and technicians move here for space industry careers, adding to the city’s technical workforce.
Economic benefits include:
Detroit’s SMEs partner closely with big aerospace contractors on space projects. They act as tier-two and tier-three suppliers in complex supply chains, providing specialized components and services.
Large manufacturers often hand off specific tasks to local SMEs. This lets the big players focus on system integration and final assembly, while SMEs handle specialized, quick-turn manufacturing.
Partnership deals between SMEs and major contractors offer stability. These long-term contracts help small companies buy new equipment and grow their capabilities, giving them more predictable revenue.
The Michigan Economic Development Corporation backs these partnerships. They connect SMEs with big contractors and offer technical support, making the whole manufacturing ecosystem stronger.
Detroit’s space manufacturing sector looks ready for big growth. Advanced 3D printing systems, green production, and new aerospace partnerships are all on the horizon.
The city’s automotive roots give it a one-of-a-kind edge for scaling up space-based manufacturing.
Detroit manufacturers are building advanced 3D printing systems for zero-gravity environments. These machines can make spacecraft parts, tools, and replacement pieces right in orbit.
Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin team up with Detroit firms to develop automated manufacturing systems. These robots can run for months without human help.
Metal 3D printing is changing the game. Detroit’s background with automotive metals helps engineers design lighter, stronger spacecraft parts.
New materials—think carbon fiber composites and titanium alloys—perform even better in space than on Earth. No gravity means perfect crystals and stronger metal bonds.
Detroit’s assembly lines for cars are inspiring new space factories. Engineers tweak robotic systems to handle vacuum conditions and wild temperature swings.
Space manufacturing brings a shot at zero-waste production, and Detroit companies are jumping in. Materials that don’t make the cut get recycled instantly, not left as space junk.
Solar power offers endless clean energy for space factories. Detroit engineers are designing solar arrays that follow the sun for max output.
Closed-loop manufacturing reuses everything. Nothing gets tossed, since dumping waste in space is crazy expensive.
Detroit firms are also working on green rocket fuel, using space resources. They make hydrogen and oxygen from asteroids for clean-burning fuel.
Green manufacturing ideas from Earth fit perfectly in space. Detroit’s experience with tough environmental rules helps companies meet space sustainability goals.
Detroit’s automotive supply chain lays the groundwork for space manufacturing growth. Hundreds of suppliers can shift their skills to aerospace.
NASA’s push for commercial space manufacturing means new contracts for Detroit companies. Federal funding supports tech development and job training.
Private space companies need manufacturing partners as they grow. Detroit’s skilled workers and industrial base make it a magnet for these high-tech firms.
International partnerships open doors for Detroit space manufacturers. European and Asian agencies want U.S. partners for joint projects.
The city’s spot near big transportation hubs makes shipping parts to launch sites in Florida and Texas a breeze. Detroit manufacturers can support several space programs at once.

Detroit’s space manufacturing sector tackles unique production needs for aerospace and defense. Local companies focus on advanced manufacturing technologies and run specialized safety and workforce development programs.
Detroit space manufacturing companies make components for aerospace and defense systems. They produce parts for satellites, spacecraft propulsion systems, and ground-based communication gear.
Many facilities focus on precision-machined parts from advanced materials. They manufacture structural elements, electronic housings, and thermal management systems for space use.
These companies also build testing equipment and support hardware. That includes launch vehicle components and assembly tools used throughout the industry.
Space manufacturing has opened up technical jobs in Detroit. Engineers, machinists, and quality control specialists now find opportunities in this growing field.
The industry looks for workers with advanced manufacturing skills. Companies want employees who know precision tooling, materials science, and aerospace quality standards.
Training programs have popped up to get workers ready for these roles. Local manufacturers team up with technical schools to build relevant courses for space industry needs.
Detroit space manufacturers stick to strict aerospace safety protocols. They run thorough quality management systems and regular safety audits.
Facilities keep clean room environments for sensitive work. Workers get special training to handle hazardous materials and use precision equipment safely.
Companies inspect manufacturing processes regularly. They use advanced tests to make sure products meet tough aerospace safety standards.
Space manufacturing jobs usually pay more than traditional manufacturing roles. The specialized skills needed bring higher wages in Detroit.
Technical specialists and engineers earn a lot more thanks to aerospace industry standards. Even entry-level jobs start at better base salaries than typical manufacturing work.
Benefits often include more training and chances to move up. Companies invest in employee development to keep their workforce skilled.
Detroit manufacturers have come up with advanced materials processing for space. They make lightweight parts that survive wild temperature swings in orbit.
Local companies build new propulsion system components. These include specialized valves, fuel management systems, and structural pieces for spacecraft.
Detroit facilities also improve manufacturing processes. They invent more efficient ways to build complex aerospace parts and assemblies.
Detroit space manufacturers team up with local universities on materials research projects. They focus on coming up with new alloys and composites for aerospace work.
Some companies join forces with technical colleges to build workforce development programs. They bring in equipment and share their know-how so students can learn advanced manufacturing skills.
Research teams dig into automation and precision manufacturing together. Universities and companies pool their resources, hoping to push space manufacturing technologies forward.